Troubleshooting Results
When a run ends prematurely, the Run Status dialog will indicate the run was unsuccessful and direct the user to the Status Report for details. The Status Report will include an error statement, code, and description of the problem (e.g., ERROR 138: Node TG040 has initial depth greater than maximum depth). See Appendix D for a description of SWMM’s error messages. Even if a run completes successfully, one should check to ensure that the results are reasonable. The following are the most common reasons for a run to end prematurely or to contain questionable results.
Unknown ID Error Message
This message typically appears when an object references another object that was never defined. An example would be a subcatchment whose outlet was designated as N29, but no such subcatchment or node with that name exists. Similar situations can exist for incorrect references made to Curves, Time Series, Time Patterns, Aquifers, Snow Packs, Transects, Pollutants, and Land Uses.
Files Errors
File errors can occur when:
- A file cannot be located on the user's computer.
- A file being used has the wrong format.
- A file being written cannot be opened because the user does not have write privileges for the directory (folder) where the file is to be stored.
SWMM needs to have write privileges for a directory (folder) where temporary files are stored during a run. The original default is the directory where Windows writes its temporary files. If this directory does not exist or the user does not have write privileges to it, then a new directory must be assigned by using the Program Preferences dialog.
Drainage System Layout Errors
A valid drainage system layout must obey the following conditions:
- An outfall node can have only one conduit link connected to it.
- A flow divider node must have exactly two outflow links.
- Under Kinematic Wave routing, a junction node can only have one outflow link and a regulator link cannot be the outflow link of a non-storage node.
- Under Dynamic Wave routing there must be at least one outfall node in the network.
An error message will be generated if any of these conditions are violated.
Excessive Continuity Errors
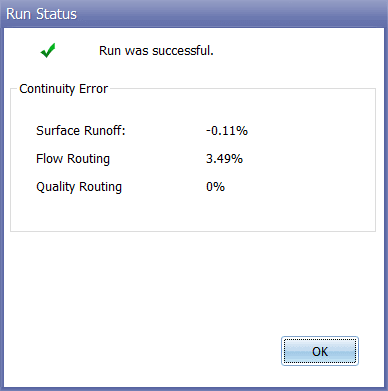
When a run completes successfully, the mass continuity errors for runoff, flow routing and pollutant routing will be displayed in the Run Status window. These errors represent the percent difference between initial storage + total inflow and final storage + total outflow for the entire drainage system. If they exceed some reasonable level, such as 10 percent, then the validity of the analysis results must be questioned. The most common reasons for an excessive continuity error are computational time steps that are too long or conduits that are too short.
In addition to the system continuity error, the Status Report produced by a run will list those nodes of the drainage network that have the largest flow continuity errors. If the error for a node is excessive, then one should first consider if the node in question is of importance to the purpose of the simulation. If it is, then further study is warranted to determine how the error might be reduced.
Unstable Flow Routing Results
Due to the explicit nature of the numerical methods used for Dynamic Wave routing (and to a lesser extent, Kinematic Wave routing), the flows in some links or water depths at some nodes may fluctuate or oscillate significantly at certain periods of time as a result of numerical instabilities in the solution method. SWMM does not automatically identify when such conditions exist, so it is up to the user to verify the numerical stability of the model and to determine if the simulation results are valid for the modeling objectives. Time series plots at key locations in the network can help identify such situations as can a scatter plot between a link’s flow and the corresponding water depth at its upstream.
Numerical instabilities can occur over short durations and may not be apparent when time series are plotted with a long time interval. When detecting such instabilities, it is recommended that a reporting time step of 1 minute or less be used, at least for an initial screening of results.
The run’s Status Report lists the links having the five highest values of a Flow Instability Index (FII). This index counts the number of times that the flow value in a link is higher (or lower) than the flow in both the previous and subsequent time periods. The index is normalized with respect to the expected number of such ‘turns’ that would occur for a purely random series of values and can range from 0 to 150.
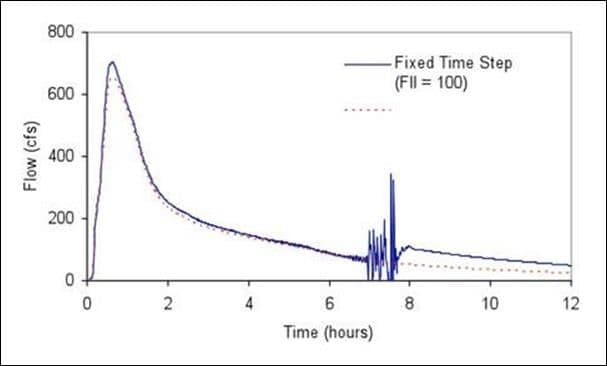
As an example of how the Flow Instability Index can be used, consider the Figure shown above. The solid line plots the flow hydrograph for the link identified as having the highest FII value (100) in a dynamic wave flow routing run that used a fixed time step of 30 seconds. The dashed line shows the hydrograph that results when a variable time step was used instead, which is now completely stable.
Flow time series plots for the links having the highest FII’s should be inspected to ensure that flow routing results are acceptably stable.
Numerical instabilities under Dynamic Wave flow routing can be reduced by:
- Reducing the routing time step
- Utilizing the variable time step option with a smaller time step factor
- Selecting to ignore the inertial terms of the momentum equation
- Selecting the option to lengthen short conduits.
