Working with GeoSWMM 2D Project
GeoSWMM 2D Modeling requires to migrate a 1D model to 2D model to access the 2D tools, and provides options to develop and simulate the simple hydraulic and hydrologic modeling allowed in SWMM to analyze complex physical landscapes. GeoSWMM has integrated a sequence of tools which streamline the process from define boundary condition to creation of the required layers and attributes for 2D model. To develop 2D flood model, it is recommended to generate all the 2D layers using GeoSWMM. All the Detailed features of these tools have been described in Development of GeoSWMM 2D Project. The available tools under the GeoSWMM 2D Menu are:
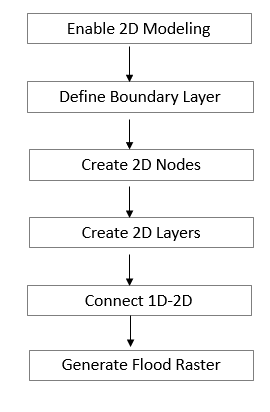
- Enable 2D Modeling
- Define Boundary Layer
- Create 2D Nodes
- Create 2D Layers
- Connect 1D – 2D
- Generate Flood Raster
Migrate to 2D Model convert the 1D Model to 2D Model and generate following 2D layers within the project database:
- Boundary Layer
- Nodes 2D
- Junction 2D
- Conduit 2D
- Cell 2D
- Orifice 2D
- Weir 2D
Define Boundary Layer tool will assist to generate polygon features in Boundary Layer as boundary condition for extent of 2D grid.
Create 2D Nodes tool will create 2D point features in Nodes 2D layer.
Create 2D Layers tool will create features into the Junction 2D, Conduit 2D and Cell 2D layers.
Connect 1D-2D tool will develop connection between 1D and 2D domain by creating features in Orifice 2D/ Weir 2D layers or with direct connection.
Generate Flood Raster tool will help the user to export raster file for Maximum Flood Depth and Water Surface Elevation for within the boundary area.
Thus, the sequence and process to be followed to develop 2D model is:
Pre-requisite Layers and Conditions for 2D model
Initial conditions to develop a GeosWMM 2D project are:
- Simulated 1D Model: A simulated 1D model is required to develop 2D modeling in GeoSWMM2D.It is a prerequisite to enable 2D flood modeling. The 1D model needs to be calibrated to generate reasonable results in 2D surface flow.
- Boundary Layer: This layer will extend to the approximate boundary at which the user anticipates surface ponding. Boundary layer can be represented by a polygon feature layer. Based on land use pattern a boundary layer can have multiple polygon features. Each feature may have different attributes. For instance, river and floodplain can be represented with two different polygon features and have different attributes. User can generate fine resolution hexagonal cell type for the river and coarse resolution hexagonal cell type for floodplain. GeoSWMM 2D provides tool to generate boundary layer and assign attribute with ease.
- Obstruction Layer: This layer defines all the structures and interventions inside the watershed that will restrict the water flow. It is an optional layer. Obstruction layer can be buildings, embankments, flood wall or any structure that affects the freely moving water flow. In GeoSWMM, 2D only polygon features can be used to introduce obstruction layers.
- Digital Elevation Model: Digital Elevation Model (DEM) is the digital representation of the land surface elevation with respect to any reference datum. It is required to extract the invert elevation of 2D nodes and determine the overland flow path. Only .tiff format is allowed as the DEM layer.
Enable GeoSWMM 2D Modeling
Any 2D modeling approach requires preparing the flood plain and flow paths over the land using the topography of the area. To do the task with accuracy, and maintain and manage a separate 2D model within GeoSWMM project, it’s necessary to enable 2D modeling at the same GeoSWMM 1D project workspace. Only after the successful migration, GeoSWMM will allow the user to access, define, create and update the corresponding layers using GeoSWMM 2D Modeling tools. As mentioned before, a simulated 1D model is pre-requisite for initiating the development of a 2D project. To migrate the 1D project to 2D project:
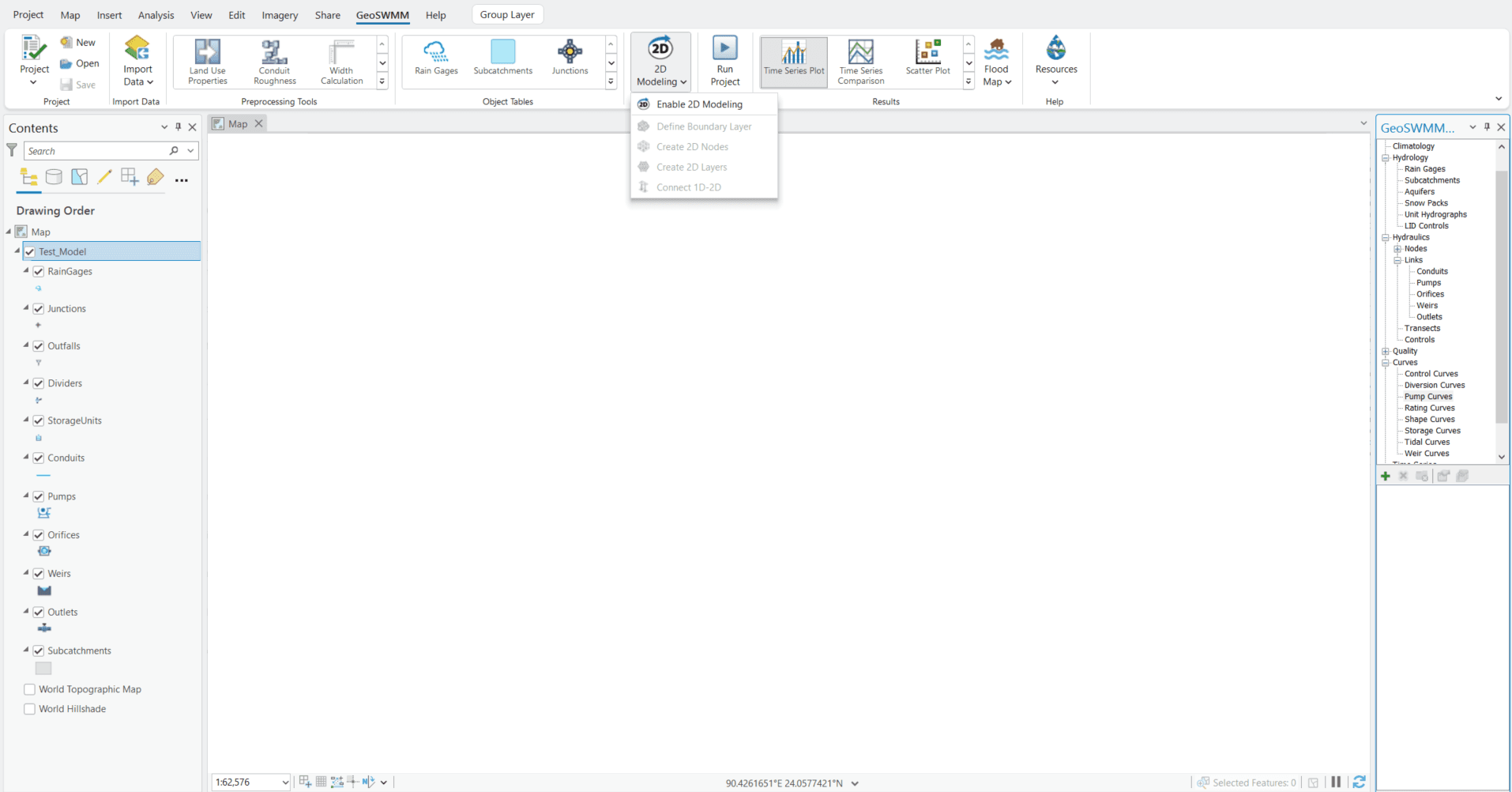
- Click 2D Modeling dropdown from GeoSWMM menu bar
- Click Enable 2D Modeling option. (Enable 2D modeling Icon)

![]() Tips
Tips
Once user enable 2D modeling, the 1D GeoSWMM project database will be converted to 2D project in the same workspace. User can keep a copy of the GeoSWMM 1D Project using the available “Save a copy” option from project menu. This GeoSWMM 2D version doesn’t allow users to go back to its native 1D model.
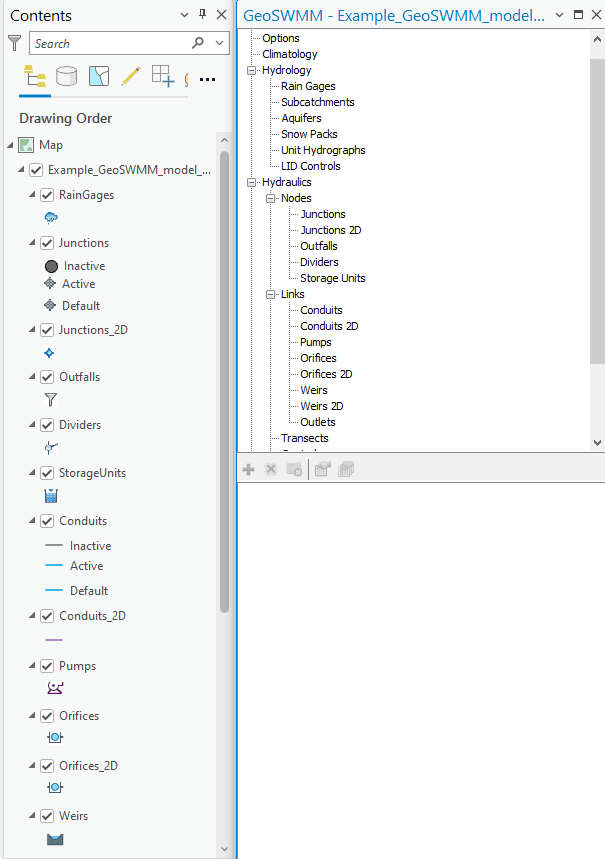
After enabling the 2D modeling, all the required 2D layers will be generated and 1D model will convert to 2D model. Note that the generated 2D layers will not contain any feature until the process framework is followed.
Set Project Defaults for Boundary Layer
Each GeoSWMM 2D project has a set of default values unless the GeoSWMM user overrides them. For any 2D project, a default values tab Boundary Layer is in the Project Defaults dialog form with other standard tabs. To set default values for a GeoSWMM 2D project:
- Go to the Settings in the menu bar and select Project Defaults.
- The Project Defaults dialog will appear. Boundary layer default values are grouped under the Boundary Layer tab.
- Set the desired values of respective parameters and click “OK” to save the settings.
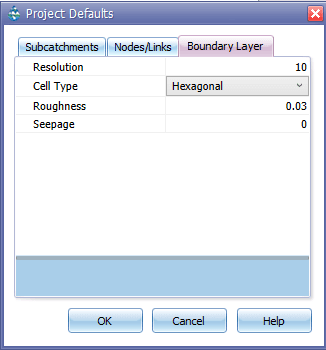
These parameters are used in defining boundary layer properties and creating corresponding 2D layers. If the user does not change the default values for these parameters and save them, boundary layer features will have these properties, and 2D layers, e.g., junctions, conduits etc. will be created as per these properties. User can override the default values from the Define Boundary Layer tool.
Table 11.1 : Definition and default attribute values for Boundary Layer
Boundary Layer Attributes | Default Value | Detail | |
|---|---|---|---|
Resolution | US Customary | SI Metric | Size of each cell |
10 | 3 | ||
Cell Type | Hexagonal | Type of cell geometry | |
Roughness | 0.03 | Manning’s roughness coefficient | |
Seepage | 0 | Rate of seepage loss into the surrounding soil | |
